Thermodynamics
Mole
The mole $N$ is a measurement for the amount of substance of a system.
Unit
$$ [N] = mol $$Avogadro number
The Avogadro number $N_A$ is the number of particles in 1 mole of 12$g$ of $\ce{^12C}$.
$$N_A = 6.022 \cdot 10^{23}$$Pressure
When a force $\overrightarrow{F}$ with the perpendicuar component $F_{\bot}$ is applied on a surface $A$, we can define the pressure $P$ exerted on the surface $A$ as:
Formula
$$ P = \frac{F_{\bot}}{A} $$Unit
$$ [P] = \frac{N}{m^2} = Pa $$ $$ Pa,\ Pascal $$Remark
Pressure is a scalar quantity.
Pressure units
Pressure has a lot of weird units that have historical or practical significance. See: Exotische Umwandlungen.
Critical Temperature
The critical temperature $T_c$ is the temperature where above the critical temperature the system cannot liquify anymore, no matter how much the pressure is increased.
Triple point of Water
The triple point for water is the temperature and pressure where the 3
phases of water, vapour, liquid, gas, coexists at the same time.
This occurs for $T=0.01^{\circ}C$ and $P=611Pa$
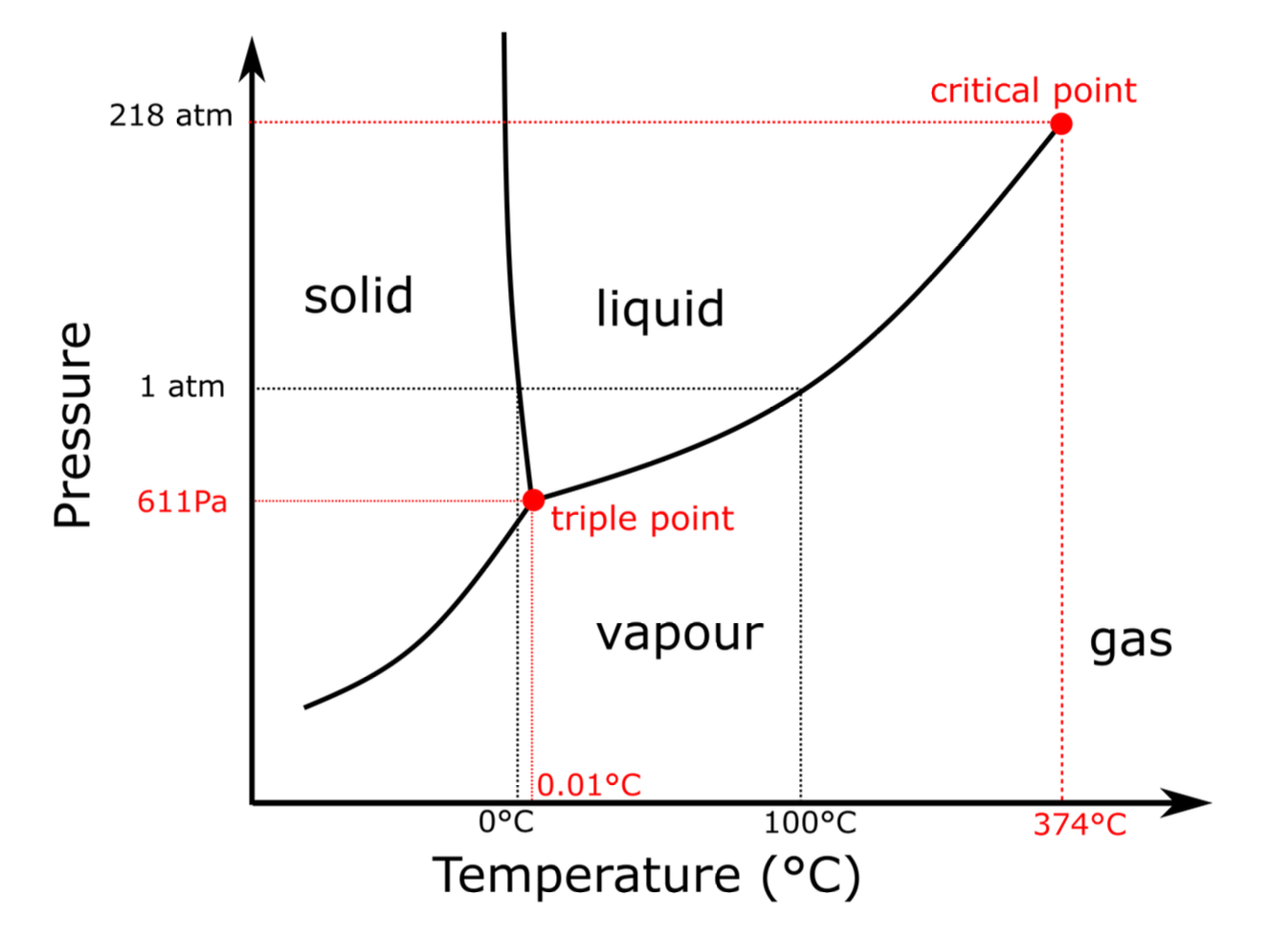
Gas and vapour
The terms gas and vapour cannot be used interchangeably:
-
Vapour:
We use the term vapour to describe a thermodynamic situation in which a system can be condensed just by decreasing pressure, keeping the temperature fixed.
-
Gas:
A gas is what we obtain by heating a vapour or a liquid above the critical temperature.
Gas universal constant
$$ R=8.314 \frac{J}{mol \cdot K} $$Perfect gas
Perfect gas has the following properties:
-
the dimension of each particle is much smaller that the volume of the container
-
the particles can only interact through elastic collisions
-
the particles occupy uniformously the volume of the container
-
there are no favoured directions in which motion can occur. The particles can move in every direction